Table of Contents
Objectives of Pyruvate Broth Test
- To determine the ability of an organism to utilize pyruvate.
- 它帮助区分Enterococcus faecalisandEnterococcus faecium.
Principle of Pyruvate Broth Test
In the identification of microorganisms, the widely used method is the ability of bacteria to form organic compounds by metabolizing certain carbohydrates and related compounds. Pyruvate broth is a carbohydrate-free, nutrient-limited medium. Pyruvate Broth contains casein peptone, sodium chloride, yeast extract, dipotassium phosphate, sodium pyruvate, and bromothymol blue. Casein peptone and yeast extract provide the nutrients andgrowth factorsnecessary for growth and the sodium chloride maintains osmotic balance. Sodium pyruvate is added as the fermentable ingredient and dipotassium phosphate is added as a buffering system. Bromothymol blue is the acid-base indicator and it is greenish-blue at an alkaline pH, and shifts to yellow when acid is produced during the fermentation of the pyruvate. Pyruvate is the active substrate and those organisms that can utilize pyruvate can break downthe substrate generating metabolic acids which aredetected by the pH indicator bromothymol blue. Acid production causes a decrease in pH which results in a color shift in the medium. When sufficient acid is generated the medium changes from a blue-green coloration to yellow. No color change in the medium is indicative of the negative reaction.
Media (Pyruvate broth)
Pancreatic digest of casein (10 gm/L),
sodium pyruvate (10 gm/L),
yeast extract (5 gm/L),
dipotassium Phosphate K2HPO4 (5 gm/L),
NaCl (5 gm/L),
bromothymol blue (0.04 gm/L),
pH 7.3 +/- 0.2 at 25ºC.
Procedure of Pyruvate Broth Test
- Inoculate the pyruvate broth tubes with an 18-24 hour culture of the organism.
- Incubate tubes at 35°-37°C in ambient air.
- Examine tubes daily for up to 5 days for the color change in the medium.
Results of Pyruvate Broth Test
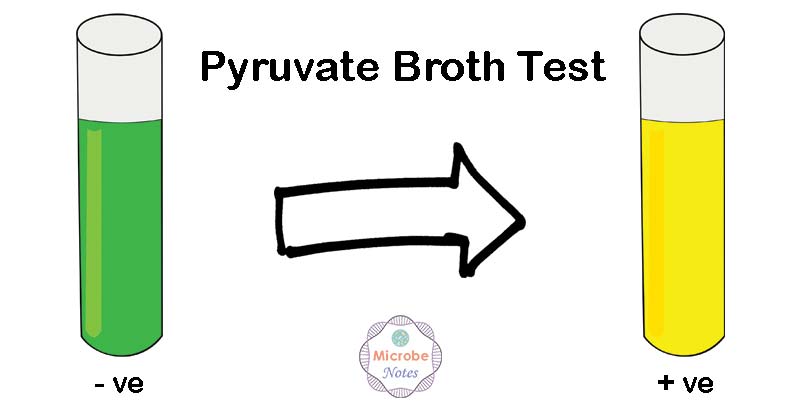
Positive test:Color change of broth from green to yellow
Negative test:No color change
Weak reaction:yellow-green coloration and should be regarded as negative
Quality Control
Positive:Enterococcus faecalis一个TCC29212
Negative:Enterococcus faecium一个TCC 6569
Negative:Streptococcus bovis一个TCC9809
References
- Tille P.M. 2014.Bailey and Scott’s diagnostic microbiology. Thirteen editions. Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 3251 Riverport Lane. St. Louis. Missouri 63043
- MacFaddin, JF. Biochemical Tests for the Identification of Medical Bacteria, 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2000.

