印迹技术是有效的技术来德tect macromolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNAs. Blot refers to the membrane on which biological molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids are immobilized.
The first invented blotting technique was Southern Blotting used for detection of DNAs by Edwin Southern in 1975. The later discovered blotting techniques are named referring to his name such as,
What is Western Blotting?
Western Blotting is an effective and widely used technique for the separation of a specific protein from a complex sample or mixture of proteins.
It is also known as immunoblotting because antibody probes are utilized to detect the target protein on the membrane.
It involves combined steps of protein lysing, electrophoresis, blotting, and antigen-antibody interaction.
Harry Towbin first described this method in 1979. This technique was called Western Blotting by W. Neal Burnette.
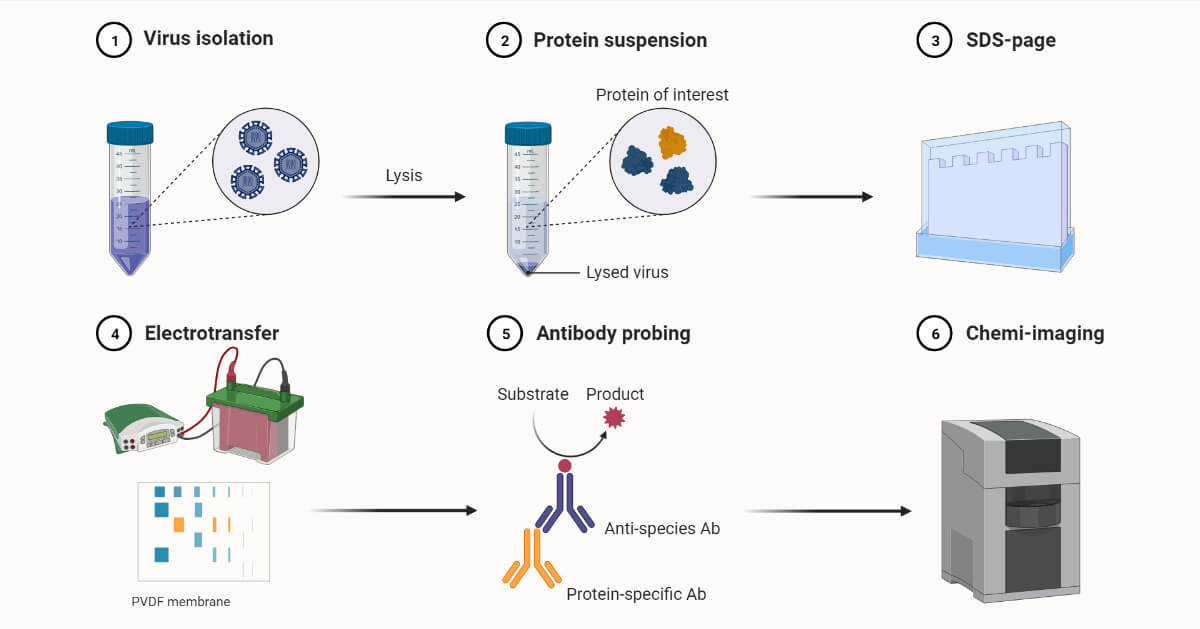
Western BlottingRequirements
- 1X Phosphate buffered saline
- 1X SDS sample buffer
- Cell lysis buffer
- Transfer buffer
- 1X TBST ( Tris-buffered saline+polysorbate 20 (Tween 20))
- Blocking buffer ( 1X TBST+ 5% non-fat dry milk)
- Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA)
- Primary Antibody Dilution Buffer ( May have 5% BSA or 5% non-fat dry milk)
- Signal fire ECL reagent ( Helps to detect even pictograms of proteins in the western blotting technique)
- Prestained protein marker
- Blotting Membrane ( Nitrocellulose paper)
- PAGE ( Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis) Set
Western BlottingPrinciple
Proteins are separated based on shape and size by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis. The separated proteins are then transferred to nitrocellulose or nylon membrane. On the membrane, they are probed with antibodies that are specific to the protein of interest. Then antigen and antibody complex formation occurs. The complex can be detected either by autoradiography or secondary antibody linked with an enzyme.
Western Blotting Procedure/Steps
Preparation of sample and protein blotting
The protein can be extracted from any type of cell or tissue by lysing them. Protease inhibitors are used to let the protein remain in its intact form without denaturation. The steps include:
- At first aspiration of cell culture media is carried out.
- Washing of the cells with PBS and aspiration of PBS is done.
- Lysing of cells by addition of 1X SDS sample buffer (100 microlitres of buffer in each well for a six-well plate) is then done.
- Transfer of extract to the microcentrifuge tube.
(Keep the cell extract on ice while performing these steps.)
(Alternatively, the cell lysis can also be done by use of 1X cell lysis buffer or 1X RIPA buffer)
- Sonication of extract for 10 to 15 sec for completion of cell lysis process.
(This step is important for decreasing the viscosity of the sample and is used for the detection of membrane-bound and nuclear proteins especially.)
- While using SDS sample buffer, 120microlitre aliquot of the sample needs to be taken and heated to 95 to 100 degrees Celcius for about 5 minutes and then is cooled on ice.
(While using cell lysis or RIPA buffer, 20 microlitre of the aliquot needs to be taken and blue or red loading buffer is added making the final concentration of 1X. Then it is heated at 95 degrees Celcius and cooled on ice.)
- The microcentrifugation of the cooled sample is carried out for 55 minutes at room temperature.
- The centrifuged sample is loaded onto a square SDS-PAGE 4-20% gradient gel.
- Loading of sample is carried along with 10 microlitres of pre-stained marker and 10 microlitres of biotinylated protein ladder.
- Then the gel is kept for the run using SDS running buffer.
Membrane Transfer
- After the gel is done, set up a transfer cassette and transfer buffer as follows- wet sponge, filter paper, gel, nitrocellulose membrane, another filter paper, and sponge. (Air bubbles if present must be removed.)
- The cassette is then closed and inserted into the transfer apparatus in the appropriate direction.
- Then it is transferred to electrophoresis under cooling conditions at 70 volts for 1.5 to 3 hours.
- After transfer nitrocellulose membrane is removed and kept to wash properly with 25ml of TBST buffer for five minutes at room temperature.
Blocking
- For the membrane blocking, it is treated with 25 ml of blocking buffer (1X TBST with 5% non-fat dry milk) at room temperature for 1 hour.
- The membrane is then again washed with 15 ml of 1X TBST.
(Different measurements are for 100 cm nitrocellulose membrane only. Volume needs to be adjusted for differently sized membranes.)
Antibody binding
- The primary antibody needs to be diluted with 10 ml of recommended dilution buffer as per the product datasheet.
- The membrane is then incubated in the diluted antibody by gentle agitation at 4 degrees Celcius for the night.
- And another day the membrane is at first washed three times for 5 minutes with about 15 ml of TBST.
- 洗涤过程后,species-appropriate HRP-linked secondary antibody is then diluted at 1 to 2000 in 10 ml of blocking buffer.
- The membrane is then incubated in the secondary antibody with gentle agitation for an hour at room temperature on an orbital shaker.
- The incubated membrane is again washed three times for five minutes each wash with 15 ml of TBST.
Detection of protein
- At the first, signal fire ECL reagent is prepared (Done by mixing one part of 2X Reagent A and one part of 2X Reagent )
- The membrane is again incubated in 10 ml of ECL reagent with gentle agitation at room temperature for one minute.
- The excess developing solution is drained out without letting the membrane dry out.
- The membrane is wrapped in a plastic rap and is exposed to X-ray film carried out in a dark room. It is done for 10 sec which is considered a proper exposure time.
- Protein bands can be observed under the X-ray film.
Western BlottingResult Interpretation
Based on the technique used for the western blotting, the proteins can be detected by use of chemiluminescence, colorimetry techniques, use of radioisotopes as done in X-ray film and use of fluorescent chemicals tagged to the secondary antibody.
The protein bands of the sample are compared with control or size markers and molecular weight in Dalton is detected to identify the protein. Digital imaging techniques are also developed for the interpretation of separated proteins.
Western BlottingApplications
- It is used as a confirmatory test for HIV.
- 决心的大小和数量的蛋白质sample
- Serodiagnosis of tubercular meningitis and neurocystocircosis
- Separation of protein from a complex mixture
- Detection of autoimmune diseases
Western BlottingAdvantages
- It can detect a very small amount (picograms) of protein in a sample.
- High sensitivity and specificity
- Most suitable and effective among other techniques for HIV detection.
Western BlottingLimitations
- It requires high skills and is hence difficult to perform.
- In some cases, the antibodies bind with other proteins than the protein of interest.
- If the primary antibody for protein of interest is not available, it can’t be detected.
- Primary antibodies are expensive.
- Small-sized proteins may not be retained by the membrane.
- The appearance of unusual bands
- The appearance of high background in the blot
References
- Ghosh, R., Gilda, J. E., & Gomes, A. V. (2014). The necessity of and strategies for improving confidence in the accuracy of western blots.Expert review of proteomics,11(5), 549–560.https://doi.org/10.1586/14789450.2014.939635
- Mahmood, T., & Yang, P. C. (2012). Western blot: technique, theory, and troubleshooting.North American Journal of medical sciences,4(9), 429–434.https://doi.org/10.4103/1947-2714.100998
- Goldsby R.A., Kindt T.J., Osborne B.A., (1999) Kuby Immunology, 4thedition, W.H.Freeman & Co Ltd.
- Parija S.C., (2009), Textbook of Microbiology and Immunology, 2ndedition, Elsevier, a division of Reed Elsevier India Private Limited

