The Brassicaceae family is commonly known as the Mustard family or Cruciferae family.It is a large family which comprises about 365 genera and 3250 species. It includes economically important plants used as vegetables, medicines, oil-yielding seeds, and ornamental purposes. In Nepal, there are 94 species from 38 genera reported.
Brassicaceae Family Distribution
- The plants of the Brassicaceae family have a global distribution.
- These plants can be found in diverse climates; primarily, most of them are found in temperate regions of the northern hemisphere.
- Many plants are cultivated for different purposes. Some species are grown for their edible parts as vegetables (Cabbage, radish, cauliflower, etc.) and other as oil yielding seeds (mustard). Additionally, certain plants are grown for ornamental purposes.
Habit and Habitat ofBrassicaceae Family
- The plants are mostly herbs which may be annual, biennial, or perennial, rarely undershrubs (e.g.,Farsetia, Jacquemontii)
- Most plants in this family are adapted to terrestrial habitats, while some are aquatic (e.g.,Nasturtium officinale)
- The plants are often characterized by their hairy appearance
- Many Brassicaceae herbs possess a pungent smell of sulfur (sulfur-containing glucosides).
Brassicaceae FamilyVegetative Characteristics
- Root:Generally possesses atap root system. However, in some species within this family, the tap root undergoes modification to store food and assumed different shapes. Two common modified tap root forms found in this family arefusiform(radish),napiform(turnip), etc.
- Stem:The stem are typicallyerect, majority areherbaceous而其他的arerarelywoody, typicallysolidandcylindrical,branchedorunbrancheddepending on the species, most of the plants arehairyin which the stem are covered with fine hairs known as trichomes.
- Leaf:Radical (radish) cauline and ramal, simple , alternate, margin is smooth, serrated or lobed depending on the species, exstipulate and usually lyrate.
Brassicaceae Family FloralCharacters
- Inflorescence:Racemose type
- Flower: Ebracteate, pedicellate, bisexual, complete, actinomorphic, rarely zygomorphic, tetramerous or bimerous, hypogynous, cyclic
- Calyx: 4 sepals, polysepalous, arranged in two whorls of two each, imbricate aestivation. Sepals may be caduceus, green or petalloid, inferior
- Corolla: 4 petals, polypetalous, cruciform
- Androecium: 6 stamens, polyandrous, stamens tetradynamous, arranged in two whorls, outer two stamen short while inner four stamen long, stamens having slender filaments that support the anthers at the top, the anther contain the pollen sacs where the pollen grains are produced
- Gynoecium: bicarpellary (two carpels), syncarpous, ovary superior, style short, stigma capitate, simple or bilobed, tricapellary i.e. three carpels (Lipidium), tetracarpellary i.e. four carpels (Tetrapoma)
- Fruits: Siliqua (elongated, narrow fruits with a long and slender shape) or silicula (elongated, narrow fruits with a short and broader shape)
- Pollination: cross-pollination, entomophilous, sometime self-pollination (arrangement of stamens and pistils within a flower promotes self-pollination).
- Seed: small, round to oval or elongated, non-endospermic with large curved embryo, cotyledons are oily
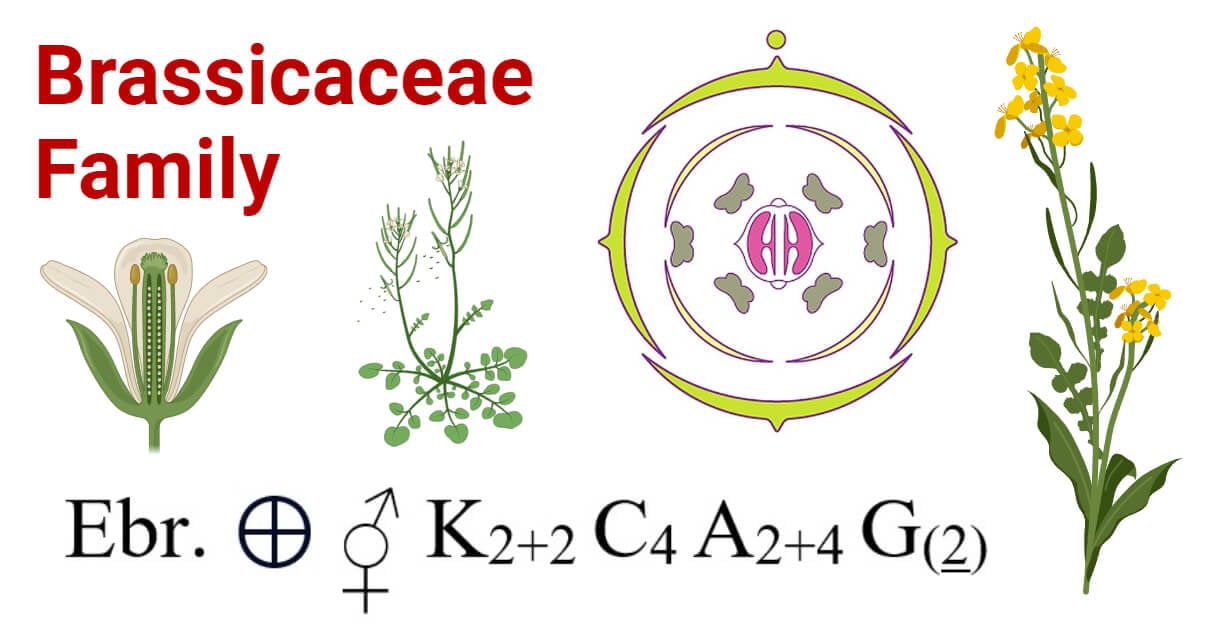
Brassicaceae Family Floral Formula
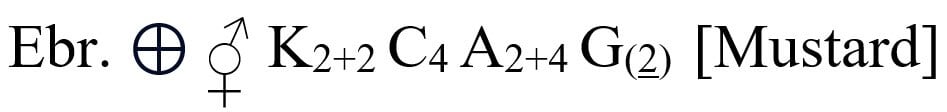
Brassicaceae Family Floral Diagram
Economic Importance of Brassicaceae Family
- Vegetables: Plants such asRaphanus sativus, Brassica rapa, Brassica junicea, Lepidium sativum,etc. are used for vegetables.
- Oils: Seeds ofBrassica campestris(mustard), Brassica juncea(Rayo), Brassica nigra(black mustard),Brassica alba(white mustard) are used for extraction of oil which is used for cooking, burning, etc.
- Cattle feed and manure: The remains of seeds after extracting oil can be used as cattle feed and manure.
- Fodder: The leaves and other parts of the species are used as fodder.
- Condiments: The seeds ofBrassica nigra, Brassica albaandBrassica junceaare used as condiments.
- Medicines: Seeds ofIberisamaraandChieranthus cheriare used in treatment of asthma and bronchitis. The seeds ofMathiola incanahas anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. The root ofLepidium sativumare effective against syphilis.
- Weeds:Capsella bursa-pastoris, Farsetia spp,etc. are common weeds of medicinal value.
- Ornamental purpose:Iberisamara(candytuft),Lunaria(honesty)andChieranthus cheri(wall flower) are used as ornamental purpose and are grown in gardens.
Brassicaceae Family Identification Characteristics
- Herbaceous plant with pungent sap having sulfur-containing glucosides.
- Leaves are covered with fine hairs called trichomes.
- Flowers ebracteate, bimerous or tetramerous, bisexual, actinomorphic, and hypogynous
- Calyx contains four sepals, polysepalous arranged in two whorls.
- Corolla contains four petals, polypetalous
- Stamens are six in number, polyandrous
- Stamens are associated with green nectaries
- Carpels are two in number (Bicarpellary), syncarpous, ovary superior, and parietal placentation.
- Fruits siliqua or silicula
- Seed non-endospermic with the curved embryo.
Some common Plants of Brassicaceae Family
- Mustard:Brassica campestris
- 萝卜:Raphanus sativus
- Cauliflower:Brassica oleracea var botrytis
- Cabbage:Brassica oleracea var capitata
- Turnip:Brassica rapa
- Candytuft:Iberis amara
- Black mustard:Brassica nigra
- Shepherd’s purse:危害囊——pastoris
- Garden cress:Lepidium sativum
- Knol (Gyanth-gobi):Brassica oleracea var. gongylodes
References
- Keshari A.K, Ghimire K.R, Mishra B.S, Adhikari K.K (2012), A Textbook of Higher Secondary Biology, Vidyarthi Pustak Bhandar, Kathmandu, pp 463-466
- https://onlinesciencenotes.com/characteristics-economic-importance-cruciferace-brassicaceae/
- https://www.studyandscore.com/studymaterial-detail/brassicaceae-general-characters-distribution-important-plants-economic-importance-and-floral-diagram
- https://www.nativeplants.org/wp-content/uploads/brassicaceae.pdf
- http://ppup.ac.in/download/econtent/pdf/1590594035835_MSC%20SEM%20II%20MBOTCC%209%20FAMILY%20CRUCIFERAE.pdf

